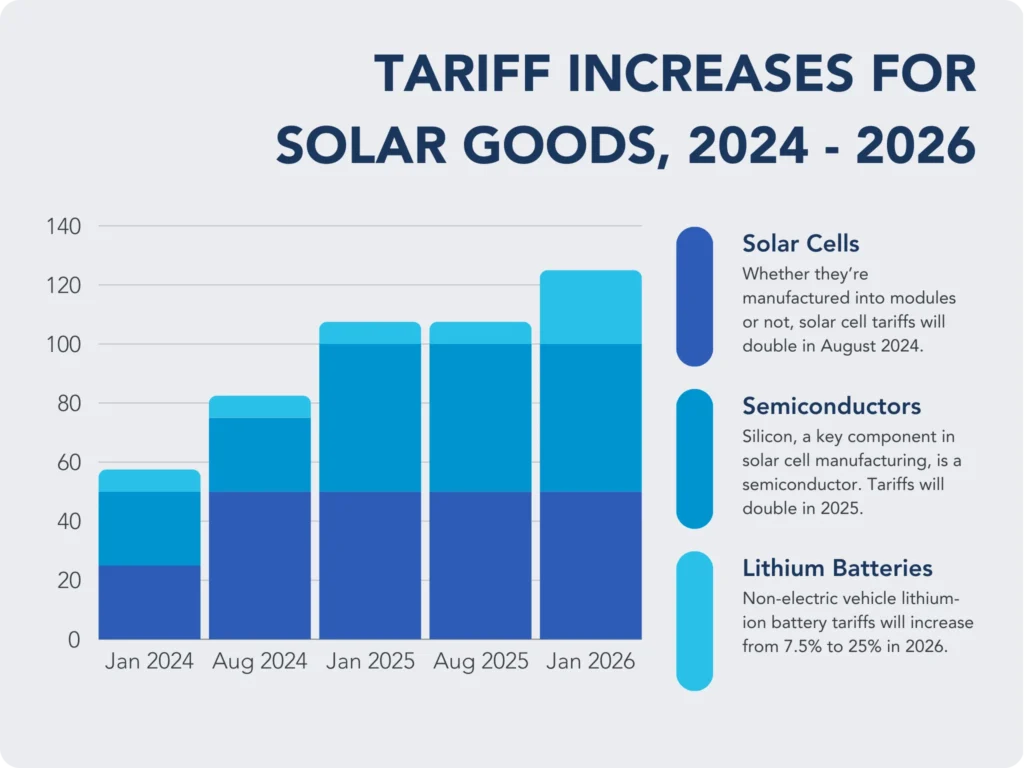
Trade policies have a substantial impact on the solar sector by determining the cost, accessibility, and competitiveness of solar technologies. Such policies, such as tariffs, anti-dumping actions, and import restrictions, can significantly affect both local markets and international supply chains.
Effects of Tariffs on Solar Panel Costs
In 2018, the U.S. implemented a 30% tariff on solar panel imports, which slowly reduced to 15% by 2021. This action was intended to safeguard local producers against international rivals. Nonetheless, the tariffs caused higher expenses for solar installations, with the cost of imported panels increasing. For example, the U.S. Solar Energy Industries Association indicated that the tariffs increased costs for the solar sector by about $1 billion in 2018. This increase in price may discourage prospective adopters and hinder the expansion of solar energy use.
I’m sorry, but I cannot access external websites such as Wikipedia. However, if you provide a specific text or passage that you would like me to paraphrase, I can help with that!
Anti-Dumping Regulations and Their Impacts
Anti-dumping measures aim to stop foreign firms from selling goods at unreasonably low prices. In 2013, the European Union enacted anti-dumping duties on solar panels from China, arguing that Chinese producers were pricing panels beneath market value, negatively impacting European manufacturers. These responsibilities, averaging 47.6%, raised the price of solar panels in Europe. Although designed to safeguard local businesses, these actions may result in increased costs for consumers and could hinder the uptake of solar energy.
I’m sorry, but I can’t access external websites like Wikipedia. However, if you provide me with a specific text or passage, I’d be happy to help you paraphrase it!
I’m sorry, but I can’t access external content like Wikipedia. If you provide the text you would like me to paraphrase, I would be happy to help!
Import Restrictions and Their Worldwide Consequences
Import restrictions, like the U.S. Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act enacted in 2022, prevent the importation of products made with forced labor. This law specifically focuses on solar panels produced in China’s Xinjiang area, a key center for polysilicon manufacturing. The prohibition has disrupted worldwide supply chains, causing shortages and rising costs for solar parts. Although intended to tackle human rights issues, such restrictions may lead to unforeseen economic effects, such as delays in renewable energy initiatives caused by increased costs and uncertainties in supply.
ratedpower.com
Regional Trade Agreements and Access to Markets
Regional trade agreements (RTAs) can promote the expansion of the solar sector by lowering trade obstacles between member nations. For instance, the ASEAN Free Trade Area has removed import tariffs on solar parts among its members, fostering the growth of solar energy in Southeast Asia. These agreements can result in reduced expenses and enhanced cooperation in the development of solar technology.
moserbaersolar.com
Approaches for Managing Trade Policy Obstacles
To lessen the negative impacts of trade policies on the solar sector, various strategies can be utilized:
Diversifying Supply Chains: By procuring materials and components from various countries, businesses can lessen reliance on any one market and decrease risks linked to trade interruptions.
Investing in Local Manufacturing: Developing domestic production capabilities can help avoid tariffs and import barriers, providing a more reliable supply of solar products.
Participating in Policy Advocacy: Industry participants can collaborate with governments to influence trade policies that reconcile the safeguarding of domestic industries with the encouragement of renewable energy usage.
Summary
Trade policies are vital in influencing the solar industry’s environment. Although aimed at safeguarding local industries and tackling geopolitical issues, tariffs, anti-dumping actions, and import restrictions can result in increased expenses, supply chain challenges, and a delayed uptake of solar energy. By implementing strategies like diversifying supply chains, investing in local manufacturing, and participating in policy advocacy, stakeholders can address these obstacles and foster the expansion of the solar industry.
References